Transmission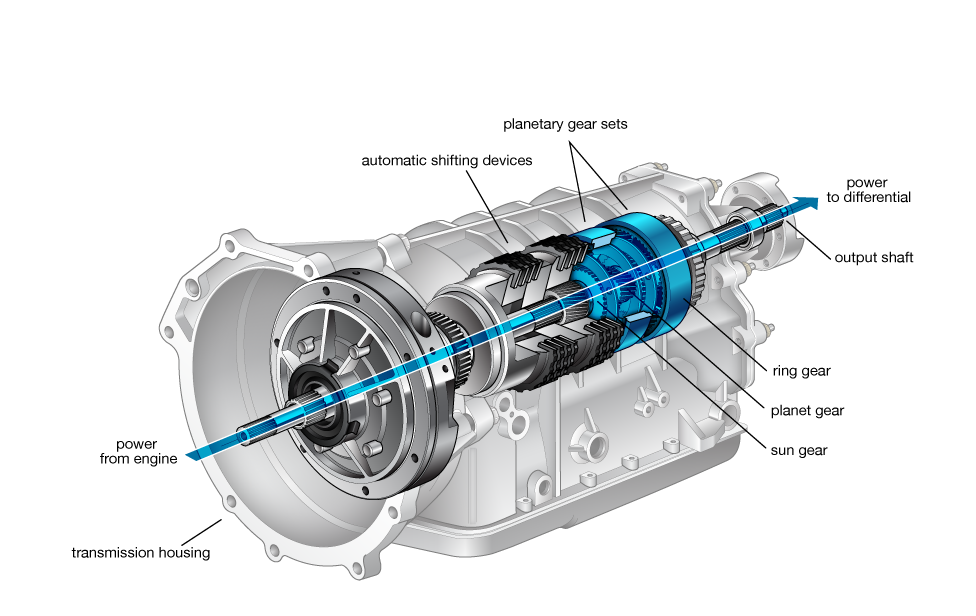
Listen, repeat, memorize!
Automatic Transmission
An automatic transmission is any transmission that doesn’t require the driver to shift gears.
There are more types of automatic transmissions than ever before, including conventional torque-converter step-gear automatics, dual-clutch automatics (sometimes called automated manuals), continuously variable automatic transmissions and hybrids.
Although different in design, their performance can be remarkably alike to the casual driver.
Though manual shifting (with paddle shifters) is now a common feature, the automatic functionality and lack of a third pedal mean that a car is an automatic.
Over the years, automatic transmissions have been gaining gears but losing dipsticks.
Current models reach as high as nine speeds, and a dipstick for checking the transmission fluid has become rare.
Many automatic transmissions are sealed or can be checked only by a mechanic.
Always refer to your car’s owner’s manual for the proper service intervals.- Listen to the Text:
Clutch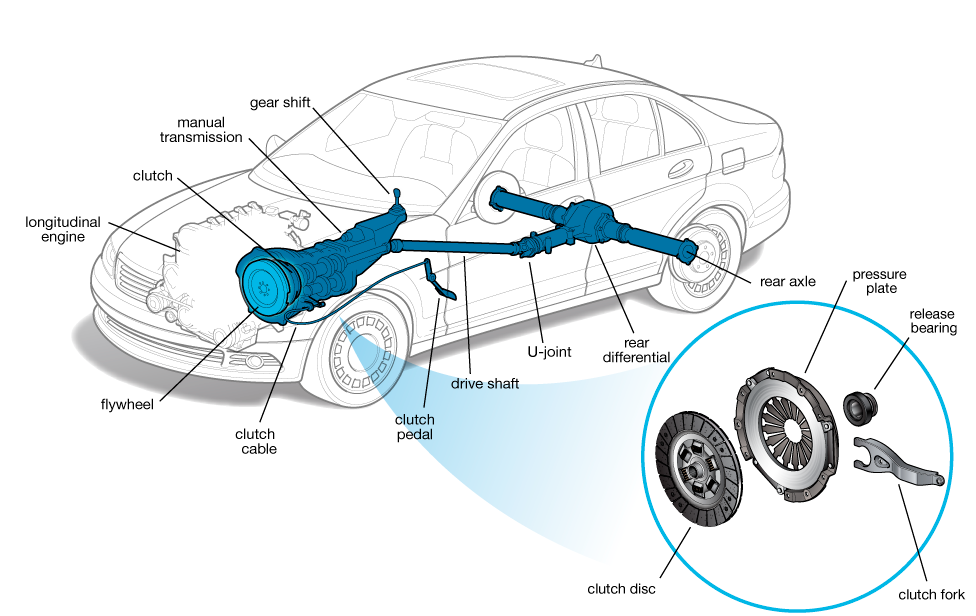
Listen, repeat, memorize!
Clutches operate behind the scenes in many transmissions, including automatics, but the word clutch typically refers to the component that connects and disconnects the engine’s rotating crankshaft to a traditional manual transmission.
It disconnects when the driver depresses the clutch pedal, selects a gear using the stick shift and re-engages when the pedal is released.
Because the clutch disk is stationary when the transmission is put into First gear or Reverse, it withstands tremendous initial friction when it contacts the engine’s spinning flywheel, moving the car forward.
It’s typical for a clutch to require replacement at least once in the car’s lifetime, depending on one’s driving style.
Clutch failure can also involve the mechanical or hydraulic connection between the pedal and the transmission.
Listen to the Text:- Transmission
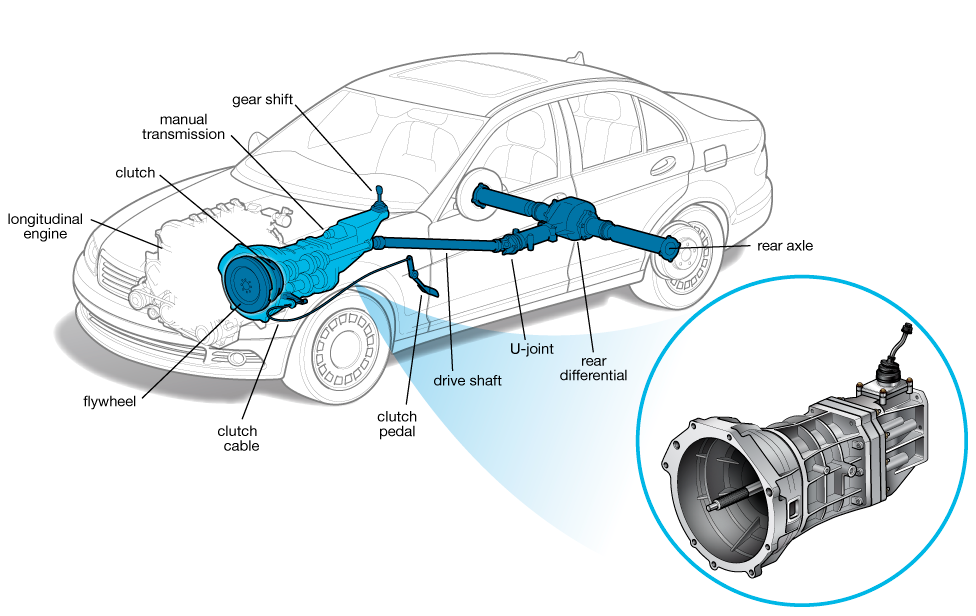
Listen, repeat, memorize!
The transmission is a mechanical component designed to transmit power from a vehicle’s engine to the drive axle, which makes the wheels drive the vehicle.
By varying the gear ratio, the transmission alters the levels of power and speed to the wheels.
The transmission serves three main roles:
1. It connects and disconnects the motor from the rest of the drivetrain (drive shafts, axles, wheels).
2. It provides gearing that allows the engine’s limited range of operation to take the car from a standstill to high speeds.
3. It allows the driver to change direction from forward to backward.
Additionally, transmissions can serve to hold the car in place when it’s off, either in the Park setting (automatics) or by remaining in gear (manuals).
Thanks to tech advancements for both transmissions and lubricants, many of today’s transmissions require less maintenance, or less frequent maintenance, than they used to.
Listen to the Text:- Manual Transmission
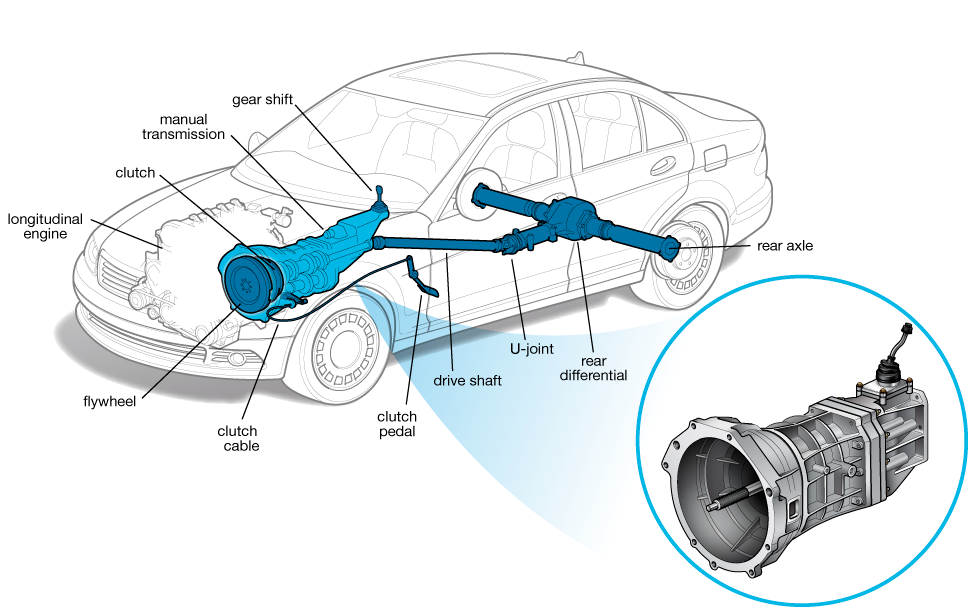
Listen, repeat, memorize!
A manual transmission is one with a stick for shifting gears and a third pedal for operating a clutch.
Many automatic transmissions now enable manual shifting, and one style is even known as an “automated manual” because of its underlying design, but their automatic operation are what set them apart from a true manual transmission.
Though manuals now can have as many as seven speeds, they remain similar under the skin.
Once the key to higher miles per gallon (mpg), manuals no longer have this advantage.
Thanks to technology and high gear counts, automatics are often more efficient and are sometimes maintenance-free.
Depending on driving style, manual transmissions tend to require clutch replacements with time and use.
Listen to the Text:
